Tool Calling in ASI:One
Tool calling lets ASI:One models go beyond text generation by invoking external tools with structured arguments you define. Use it to integrate APIs, databases, or any custom code so the model can retrieve live data, perform tasks, or trigger workflows based on user intent.
Overview
When you supply a tools array, the model may decide to call one of those tools during the conversation. The high-level flow is:
- User asks a question → the model thinks a tool is needed.
- Assistant emits a
tool_useblock specifying the tool name and arguments. - Your backend executes the real tool and sends back a
tool_resultmessage. - Assistant incorporates that result into its final reply.
ASI:One Model Variants
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
asi1-mini | Balanced performance and speed (default) |
asi1-extended | Deeper reasoning and longer context |
asi1-fast | Optimised for ultra-low latency |
asi1-graph | Tuned for analytics & auto-generation of graphs |
All variants support tool calling. Pick the one that suits your latency vs. reasoning needs.
Quick-start Example
Below is the minimal request that defines a single get_weather tool and lets the model decide whether to call it.
- Weather example
- Email example
- Knowledge-base example
- cURL
- Python
- JavaScript
curl -X POST https://api.asi1.ai/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $ASI_ONE_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "asi1-mini",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a weather assistant. When a user asks for the weather, call get_weather with the correct location string."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the current weather like in Indore right now?"}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get current temperature for a given city name.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {"type": "string", "description": "City and country e.g. Paris, France"}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
}
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 1024
}'
import os, requests, json
API_KEY = os.getenv("ASI_ONE_API_KEY")
BASE_URL = "https://api.asi1.ai/v1"
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}", "Content-Type": "application/json"}
get_weather_tool = {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get current temperature for a given city name.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"location": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
}
payload = {
"model": "asi1-mini",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Weather in Paris?"}],
"tools": [get_weather_tool]
}
resp = requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/chat/completions", headers=headers, json=payload).json()
print(json.dumps(resp, indent=2))
import fetch from "node-fetch";
const payload = {
model: "asi1-mini",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "Weather in Tokyo?" }],
tools: [
{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "get_weather",
description: "Get current temperature for a given city name.",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: { location: { type: "string" } },
required: ["location"]
}
}
}
]
};
const res = await fetch("https://api.asi1.ai/v1/chat/completions", {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json", Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.ASI_ONE_API_KEY}` },
body: JSON.stringify(payload)
});
console.log(await res.json());
- cURL
- Python
- JavaScript
curl -X POST https://api.asi1.ai/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $ASI_ONE_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "asi1-mini",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an assistant that can send emails via send_email."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Can you send an email to ilan@example.com and katia@example.com saying hi?"}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "send_email",
"description": "Send an email to a given recipient with a subject and message.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"to": {"type": "string", "description": "Recipient email address"},
"subject": {"type": "string", "description": "Email subject line"},
"body": {"type": "string", "description": "Body of the email message"}
},
"required": ["to", "subject", "body"],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}
}
]
}'
import os, requests, json
API_KEY = os.getenv("ASI_ONE_API_KEY")
BASE_URL = "https://api.asi1.ai/v1"
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}", "Content-Type": "application/json"}
send_email_tool = {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "send_email",
"description": "Send an email via SMTP or any provider.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"to": {"type": "string"},
"subject": {"type": "string"},
"body": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["to", "subject", "body"]
}
}
}
payload = {
"model": "asi1-mini",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Email hi to ilan@example.com"}],
"tools": [send_email_tool]
}
resp = requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/chat/completions", headers=headers, json=payload).json()
print(json.dumps(resp, indent=2))
// Using fetch in Node.js
import fetch from "node-fetch";
const payload = {
model: "asi1-mini",
messages: [
{ role: "user", content: "Email hi to ilan@example.com" }
],
tools: [
{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "send_email",
description: "Send email",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
to: { type: "string" },
subject: { type: "string" },
body: { type: "string" }
},
required: ["to", "subject", "body"]
}
}
}
]
};
const res = await fetch("https://api.asi1.ai/v1/chat/completions", {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json", Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.ASI_ONE_API_KEY}` },
body: JSON.stringify(payload)
});
console.log(await res.json());
- cURL
- Python
- JavaScript
curl -X POST https://api.asi1.ai/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $ASI_ONE_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "asi1-mini",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You can look up answers in an internal knowledge base via search_knowledge_base."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Can you find information about ChatGPT in the AI knowledge base?"}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "search_knowledge_base",
"description": "Query a knowledge base to retrieve relevant info on a topic.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string", "description": "Search query"},
"options": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"num_results": {"type": "number", "description": "Number of top results"},
"domain_filter": {"type": ["string","null"], "description": "Optional domain filter"},
"sort_by": {"type": ["string","null"], "enum": ["relevance","date","popularity","alphabetical"], "description": "Sorting"}
},
"required": ["num_results","domain_filter","sort_by"],
"additionalProperties": false
}
},
"required": ["query","options"],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}
}
]
}'
import os, requests, json
API_KEY = os.getenv("ASI_ONE_API_KEY")
BASE_URL = "https://api.asi1.ai/v1"
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}", "Content-Type": "application/json"}
search_tool = {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "search_knowledge_base",
"description": "Search KB",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string"},
"options": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"num_results": {"type": "number"},
"domain_filter": {"type": ["string","null"]},
"sort_by": {"type": ["string","null"], "enum": ["relevance","date"]}
},
"required": ["num_results","domain_filter","sort_by"]
}
},
"required": ["query","options"]
}
}
}
payload = {
"model": "asi1-mini",
"messages": [{"role":"user","content":"Search ChatGPT"}],
"tools": [search_tool]
}
resp = requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/chat/completions", headers=headers, json=payload).json()
print(json.dumps(resp, indent=2))
import fetch from "node-fetch";
const payload = {
model: "asi1-mini",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "Search ChatGPT" }],
tools: [
{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "search_knowledge_base",
description: "Search KB",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
query: { type: "string" },
options: {
type: "object",
properties: {
num_results: { type: "number" },
domain_filter: { type: ["string","null"] },
sort_by: { type: ["string","null"], enum: ["relevance","date"] }
},
required: ["num_results","domain_filter","sort_by"]
}
},
required: ["query","options"]
}
}
}
]
};
const res = await fetch("https://api.asi1.ai/v1/chat/completions", {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json", Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.ASI_ONE_API_KEY}` },
body: JSON.stringify(payload)
});
console.log(await res.json());
Example Assistant Response (truncated)
{
"id": "id_t0m4Pzm0KDbMg0WaX",
"model": "asi1-mini",
"choices": [
{
"finish_reason": "tool_calls",
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "",
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_WzB5g",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"Paris, France\"}"
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
At this point you execute get_weather("Paris, France"), then send back the tool_result message so the model can finish its answer.
Complete End-to-End Example
Below is a working Python script that demonstrates the full tool calling flow with ASI:One. This example uses a city-name-based weather tool that handles geocoding internally.
Step 1: Define your backend tool
import requests
def get_weather(location: str) -> float:
"""Return current temperature in °C for 'City, Country'."""
# Geocode the city name to coordinates
geo = requests.get(
"https://nominatim.openstreetmap.org/search",
params={"q": location, "format": "json", "limit": 1},
timeout=10,
headers={"User-Agent": "asi-demo"}
).json()
if not geo:
raise ValueError(f"Could not geocode {location!r}")
lat, lon = geo[0]["lat"], geo[0]["lon"]
# Get weather data
wx_resp = requests.get(
"https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast",
params={
"latitude": lat,
"longitude": lon,
"current_weather": "true",
"temperature_unit": "celsius"
},
timeout=10,
headers={"User-Agent": "asi-demo"}
)
if wx_resp.status_code != 200:
raise RuntimeError(f"Open-Meteo {wx_resp.status_code}: {wx_resp.text[:120]}")
return wx_resp.json()["current_weather"]["temperature"]
Step 2: Define the tool schema
weather_tool = {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get current temperature (°C) for a given city name.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"location": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["location"],
"additionalProperties": False
},
"strict": True
}
}
Step 3: Make the initial request
import os, json, requests
API_KEY = os.getenv("ASI_ONE_API_KEY")
BASE_URL = "https://api.asi1.ai/v1/chat/completions"
MODEL = "asi1-mini"
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Get the current temperature in Paris, France using the get_weather tool."}
]
resp1 = requests.post(
BASE_URL,
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}", "Content-Type": "application/json"},
json={"model": MODEL, "messages": messages, "tools": [weather_tool]},
).json()
choice = resp1["choices"][0]["message"]
if "tool_calls" not in choice:
print("Model replied normally:", choice["content"])
exit()
tool_call = choice["tool_calls"][0]
print("Tool-call from model:", json.dumps(tool_call, indent=2))
Step 4: Execute the tool and send result back
# Extract arguments
arg_str = tool_call.get("arguments") or tool_call.get("function", {}).get("arguments")
args = json.loads(arg_str)
print("Parsed arguments:", args)
# Execute the tool
temp_c = get_weather(**args)
print(f"Backend weather result: {temp_c:.1f} °C")
# Send the result back to ASI:One
assistant_msg = {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "",
"tool_calls": [tool_call]
}
tool_result_msg = {
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call["id"],
"content": json.dumps({"temperature_celsius": temp_c})
}
messages += [assistant_msg, tool_result_msg]
resp2 = requests.post(
BASE_URL,
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}", "Content-Type": "application/json"},
json={
"model": MODEL,
"messages": messages,
"tools": [weather_tool] # repeat schema for safety
},
).json()
if "choices" not in resp2:
print("Error response:", json.dumps(resp2, indent=2))
exit()
final_answer = resp2["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
print("Assistant's final reply:")
print(final_answer)
Example Output
Tool-call from model:
{
"id": "call_OCsdY",
"index": 0,
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"Paris, France\"}"
}
}
Parsed arguments: {'location': 'Paris, France'}
Backend weather result: 22.4 °C
Assistant's final reply:
The current temperature in Paris, France is 22.4°C. It's quite pleasant weather there right now!
Tool calling steps (diagram)
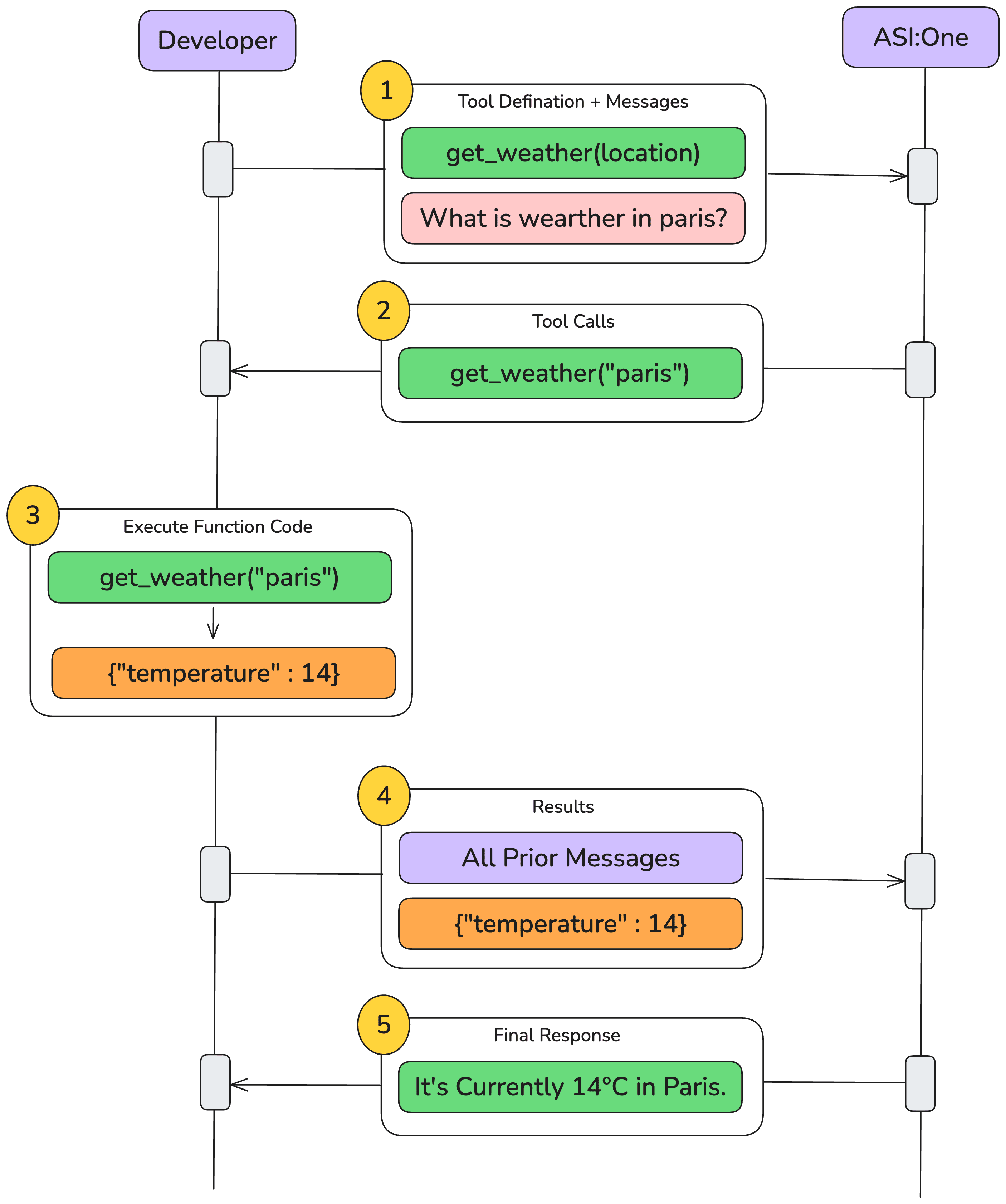
Defining tools (schema cheatsheet)
| Field | Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|
type | yes | always function |
name | yes | snake_case or camelCase |
description | yes | what & when |
parameters | yes | JSON-Schema object |
strict | optional (recommended) | enforce schema |
Handling multiple calls
for call in resp.tool_calls:
out = dispatch(call.name, json.loads(call.arguments))
messages.append({"role":"tool","tool_call_id":call.id,"content":json.dumps(out)})
Additional configs
tool_choice: "auto" (default) | "required" |{type:"function",name:"…"}| "none"parallel_tool_calls:falseto force at most one per turn.strict:trueto guarantee arguments match schema.
Best practices
- Write clear parameter docs.
- Keep fewer than 20 active tools.
- Validate inputs & handle errors gracefully.
- Log every request / result for debugging.